9 8 second row diatomic molecules
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re looking to understand the fundamental workings of chemical systems, it’s essential to know how to draw molecular orbital diagrams. These diagrams allow us to visualize the interactions between different atoms and molecules, making it possible to understand their properties and behavior. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of molecular orbital diagrams and how to create them.
For many people, the idea of creating a molecular orbital diagram can be intimidating. The process can seem complex and overwhelming, especially if you don’t have a lot of experience in chemistry. However, once you understand the basic concepts, drawing molecular orbital diagrams can be a straightforward process.
The purpose of a molecular orbital diagram is to show the different molecular orbitals that are present in a molecule or complex. These orbitals are created as a result of the interactions between different atoms, and they determine the molecule’s properties and behavior. By examining the diagram, you can determine the bond order between two atoms, the relative energy levels of the orbitals, and the magnetic properties of the molecule.
In summary, creating a molecular orbital diagram is all about understanding the different orbitals that are present in a molecule and how they interact with each other. By examining the diagram, you can gain a deeper understanding of the molecule’s properties and behavior.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams
Creating a molecular orbital diagram can seem daunting at first, but the process can be broken down into several simple steps.
Step 1: Determine the Number of Electrons in the Molecule or Complex
The first step in creating a molecular orbital diagram is to determine the number of electrons that are present in the molecule or complex. You can do this by adding up the total number of valence electrons for all of the atoms in the system.
For example, if you were creating a molecular orbital diagram for the molecule Li2, you would start by adding up the valence electrons for lithium. Lithium has one valence electron, so the total number of valence electrons in Li2 would be two.
Step 2: Create the Molecular Orbital Diagram
The second step in creating a molecular orbital diagram is to actually construct the diagram. To do this, you’ll need to draw a horizontal line that represents the different energy levels of the orbitals for the molecule. The lowest-energy orbitals are typically drawn at the bottom of the diagram, while the highest-energy orbitals are drawn at the top.
Next, you’ll need to add the valence electrons to the diagram. Electrons are represented as arrows, and they are placed in the different orbitals as based on their spin and energy level. You should start by filling the lowest-energy orbitals first before moving on to the higher-energy orbitals.
Step 3: Analyze the Molecular Orbital Diagram
Once you’ve constructed the molecular orbital diagram, you can start to analyze it. You’ll want to examine the diagram for features such as bond order and the relative energies of the orbitals.
Step 4: Repeat the Process for More Complex Molecules
If you’re working with a more complex molecule or complex, you can repeat the process described above to create a molecular orbital diagram. However, you may need to use more advanced techniques to determine the energy levels and interactions between the different orbitals.
The Importance of Molecular Orbital Diagrams
Molecular orbital diagrams are a critical tool in the study of chemistry. By visualizing the different orbitals and their interactions, we can gain a better understanding of the properties and behavior of complex molecules and reactions. These diagrams are used in a variety of areas of chemistry, including organic, physical, and inorganic chemistry, as well as biochemistry and materials science.
Question and Answer
Q: Why are molecular orbital diagrams important?
A: Molecular orbital diagrams are critical tools in the study of chemistry. They allow chemists to visualize the different interactions between atoms and molecules, which can help to provide a better understanding of their properties and behavior.
Q: What is the purpose of a molecular orbital diagram?
A: The purpose of a molecular orbital diagram is to show the different molecular orbitals that are present in a molecule or complex. These orbitals are created as a result of the interactions between different atoms, and they determine the molecule’s properties and behavior. By examining the diagram, you can determine the bond order between two atoms, the relative energy levels of the orbitals, and the magnetic properties of the molecule.
Q: What information can you obtain from a molecular orbital diagram?
A: By examining a molecular orbital diagram, you can gain information about the bond order between two atoms, the relative energy levels of the orbitals, and the magnetic properties of the molecule. You can also use the diagram to understand the overall properties and behavior of the molecule.
Q: How is the number of electrons in a molecule or complex determined?
A: The number of electrons in a molecule or complex can be determined by adding up the total number of valence electrons for all of the atoms in the system. For example, if you were creating a molecular orbital diagram for the molecule Li2, you would start by adding up the valence electrons for lithium. Lithium has one valence electron, so the total number of valence electrons in Li2 would be two.
Conclusion of How to Draw Molecular Orbital Diagrams
Creating a molecular orbital diagram can seem intimidating at first, but with a little practice, it’s possible to master this essential tool for understanding chemical systems. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create accurate and informative diagrams that provide valuable insights into the properties and behavior of molecules and complexes.
Gallery
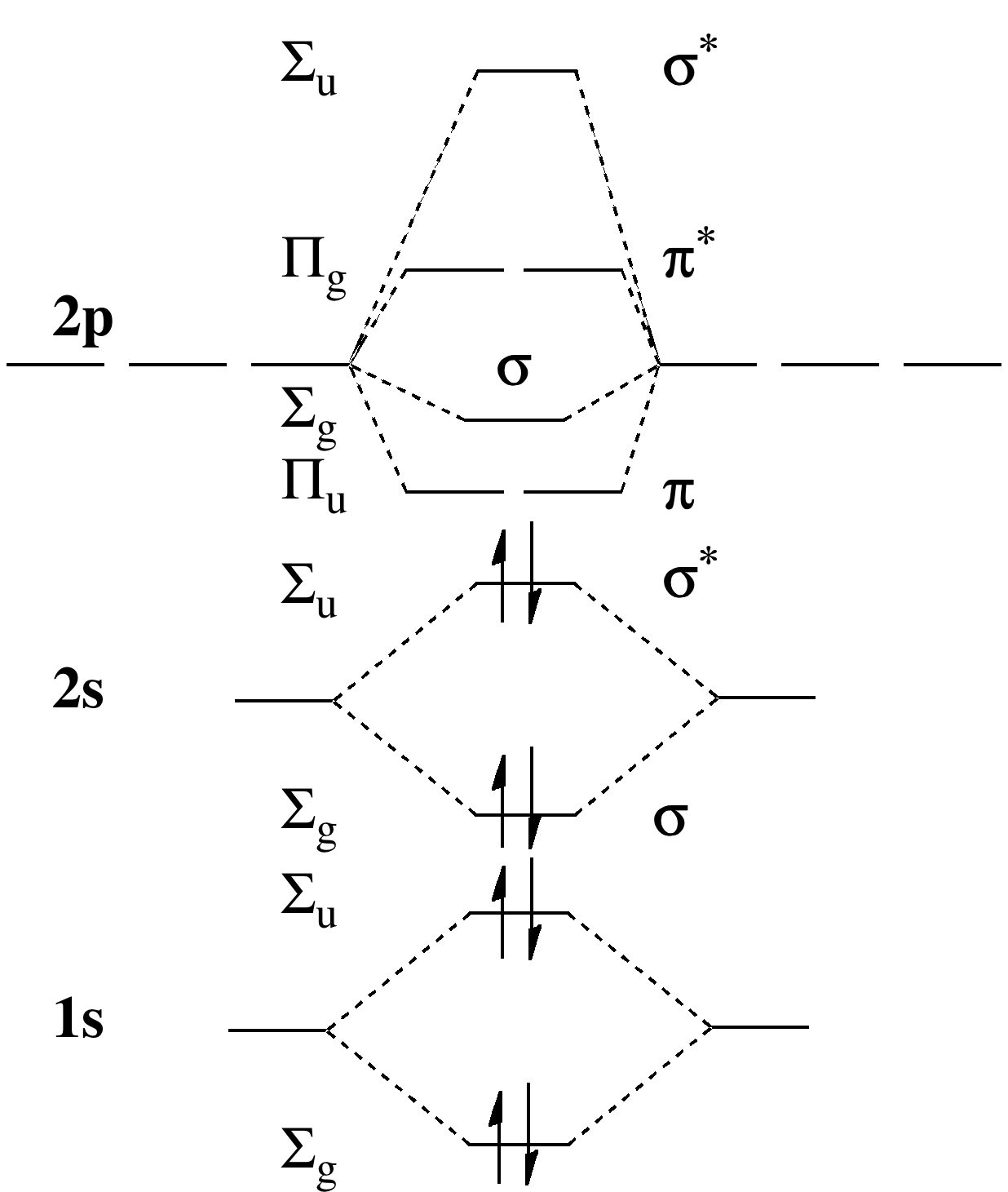
9.8: Second-Row Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry LibreTexts
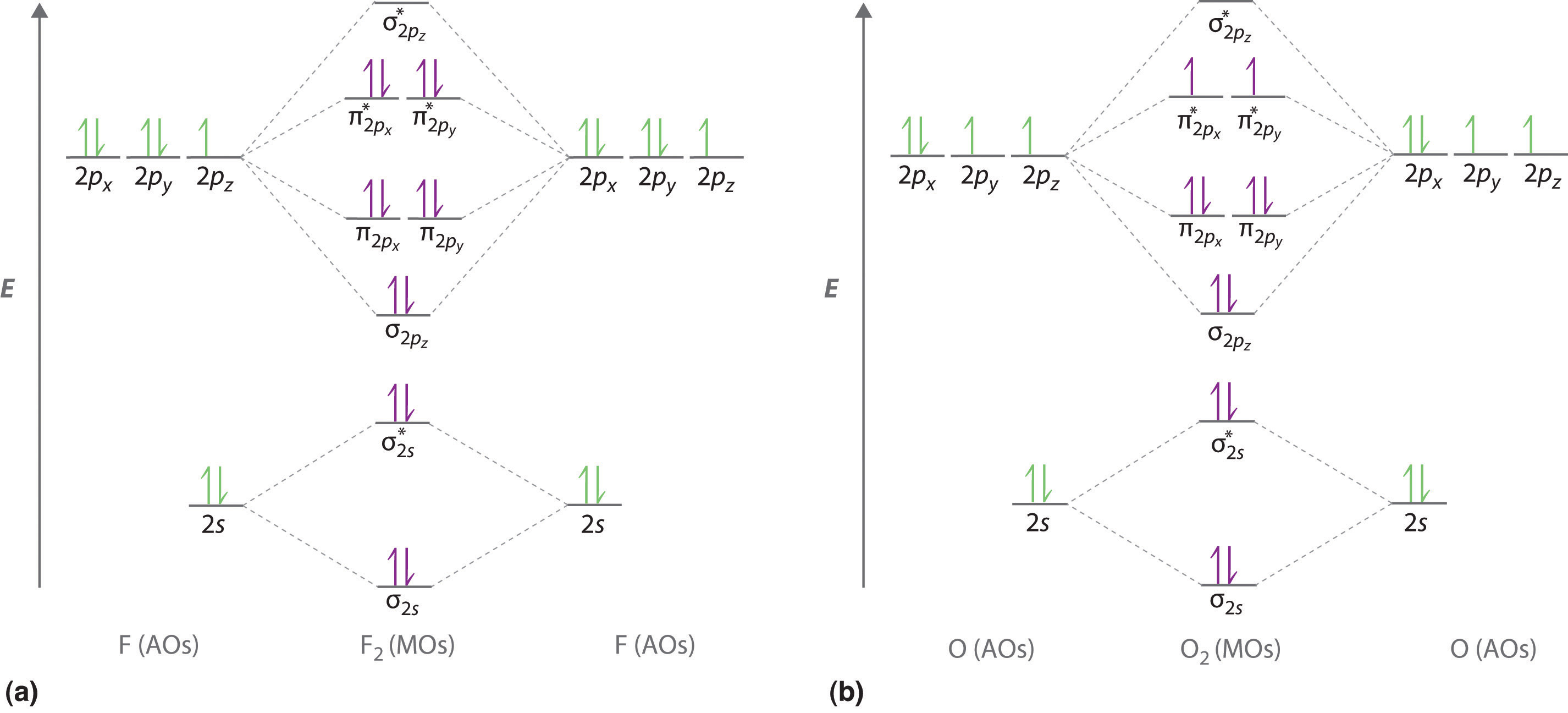
Photo Credit by: bing.com / orbital nh3 orbitals diatomic molecules of2 bonding delocalized libretexts chem homonuclear o2 valence electrons techiescientist hybridization pageindex conclusion
Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams - YouTube
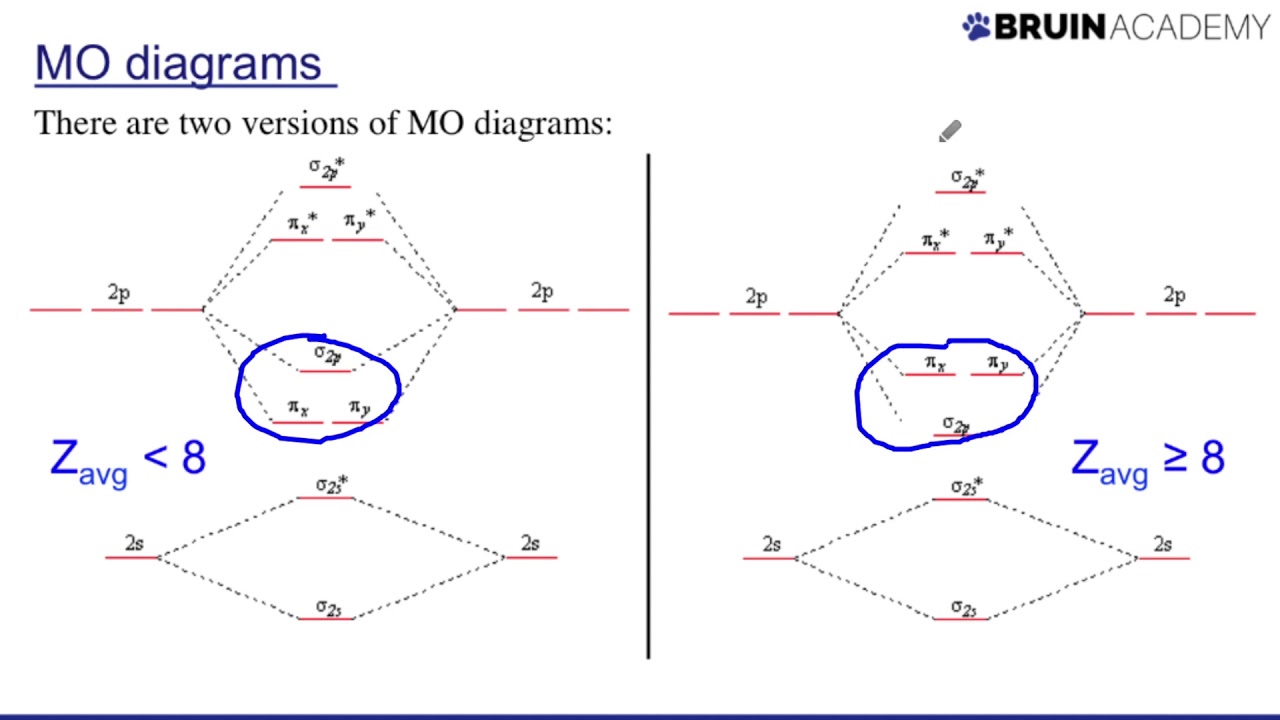
Photo Credit by: bing.com / molecular orbital diagrams
Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The

Photo Credit by: bing.com / orbital molecular diagrams determine simplified
Mathematics - Origins Of Molecular Orbital Diagrams? - History Of

Photo Credit by: bing.com / orbital molecular diagrams does origins molecules chemistry mathematics description electrons questions
Molecular Orbital Diagram For Li2

Photo Credit by: bing.com / orbital diagram molecular li2 electron configuration be2 rzepa energy draw diatomic figure henry






